Explain the Different Types of Tephra
Before we explain the different types of lava that there are we want to make a brief summary about the main characteristics of this substance. Pyroclastic flows normally hug the ground and travel downhill or spread laterally under gravity.
Tephra Fallout From The Long Lasting Tungurahua Eruptive Cycle 1999 2014 Variations Through Eruptive Style Transition And Deposition Processes Bustillos A Andean Geology
Stratovolcano Shield and Cinder Cone.

. Simulate an eruption of tephra and analyze the resulting layers. Tephra includes large rocks and small fragments such as scoria pumice and volcanic ash. The stronger eruptive types are Pelean eruptions followed by Plinian eruptions.
Magma is capable of intrusion into adjacent rocks giving rise to Sills and Dikes and extrusion onto the surface as lava and explosive ejection as Tephra to form pyroclastic rocks. Helens tephra is conspicuous as sandy material in colorful shades of orange tan yellow gray brown and white. Blocks and bombs are large pieces of tephra with a diameter of greater than 64 millimeters.
Tephra includes large rocks and small fragments such a scoria pumice and volcanic ash. Seismic waves moving along the surface of the Earth are surface waves and are the last type of seismic wave to occur. S waves occur after P and are the most damaging seismic waves.
Helens and Mount Mazama. They build up by layering lava ash and tephra. The weakest are Hawaiian and submarine then Strombolian followed by Vulcanian and Surtseyan.
Others concern the resulting shape of the eruptive products or the place where the eruptions occur. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior has been observed. Lets dive into the differences between these types of volcanoes.
It is heavier than ash. Tephra is the term used to describe rock fragments and other particles ejected from a volcano. Identify two volcanoes in the Mediterranean Belt.
Seismic waves that move below the surface of the Earth are body waves and are the first to occur. This material is known as tephra. Stratovolcanoes are tall and cone-shaped.
The largest pieces of tephra greater than 64 mm are called blocksand bombs. Tell students that once they complete this activity they can become part of the volcano fan club. Body waves are composed of two different types of waves P and S waves.
But billions of smaller and lighter pieces less than 2 mm diameter less than one tenth of an inch termed ash are carried by winds for thousands of miles. When a volcano erupts it will sometimes eject material such as rock fragments into the atmosphere. The four types of tephra are identified by size.
Several types of volcanic eruptionsduring which lava tephra ash lapilli volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissurehave been distinguished by volcanologists. Tephra in pyroclastic fall deposits may have been transported only a short distance from the vent a few meters to several km or if it is injected into the upper atmosphere may circle the globe. Its tephra typically appears darker in color than tephra from Mount St.
Indirect hazards are volcanism-induced environmental changes that lead to distress famine or habitat destruction. Gray tan or orange in color. Indirect effects of volcanism have accounted for approximately 8 million deaths during historical times.
Unfortunately the quantification of the source term is challenging and the resulting uncertainties are inherited by TTDMs particularly during syn-eruptive forecasts. Convergence plate boundaries with zones and hot spots produce different types of volcanoes. A pyroclastic flow is a fast-moving current of hot gas and rock collectively known as tephra which reaches speeds moving away from a volcano of up to 700 kmh 450 mph.
Ash is the smallest tephra. Certain types of volcanoes are associated with particular types of plate boundaries. Cinder is medium-sized tephra.
They will collect analyze and graph data before presenting results to the class. You just studied 48 terms. Ash falls from the sky and is deposited in layers on the ground.
The term tephra defines all pieces of all fragments of rock ejected into the air by an erupting volcano. Blocks and bombs are normally shot ballistically from the volcano refer to the gas thrust zone described in the direct blastsection. They produce tephra ash clouds and.
Different source term models used by TTDMs may range from simple geometric distributions to complex multicomponent and multiphase flow models see Section 36. The strongest eruptions are. Tephra is a general term for fragments of rock and lava regardless of size that are blasted into the air by explosive eruptions.
Within these wide-defining eruptive types are several subtypes. Here are some of the most common types of eruptions. Lava is magma that reaches the surface.
Mount Rainier rocks and tephra contain 55 to 64 percent silica. Most tephra falls back onto the slopes of the volcano enlarging it. Different kinds of igneous rocks.
At Mount Rainier tephra is conspicuous as sandy material in colorful shades of orange tan yellow gray brown and white. Volcanologists classify eruptions into several different types. Direct hazards are forces that directly kill or injure people or destroy property or wildlife habitat.
Sedimentary rocks form from sediments worn away from other rocks. There are two classes of volcanic hazards direct and indirect. Explain to students that they will make a series of tephra layers with household ingredients.
Instead of flat shield volcanoes like in Hawaii they have bigger peaks. At this point you might be wondering what magma is. Explain how the location of volcanoes is related to the theory of plate tectonics.
Some are named for particular volcanoes where the type of eruption is common. The gas can reach temperatures of about 1000 C. 3 Types of Volcanoes.
Tephra is a general term for fragments of rock and lava regardless of size that are blasted into the air by explosive eruptions. Some volcanoes may exhibit only one characteristic type of. Any kind of pyroclastic fall deposit will mantle or drape itself over the landscape and will decrease in both size and thickness the farther away.
The best way to achieve this goal is to start by repeating the sentence that started this post. Tephra is solid material that has been shot into the air or underwater by an explosive volcano. Mineral s crystal lized by the melt.

Introduction Professional Paper 1563 Pre 1980 Tephra Fall Deposits Mount St Helens Washington

Examples Of Tephra Fallout Structures From Volganic Plumes A Ash Download Scientific Diagram

Photographs Of Field Sites Showing Selected Tephra Deposits And Download Scientific Diagram

Volcanoes Frequency And Distribution

Volcanoes And Volcanic Eruptions

What Are Volcano Hazards Fact Sheet 002 97

The Currently Known Distribution Of Tephra And Other Volcanic Products Download Scientific Diagram

Tephra An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Volcanic Hazards Lava Flow Pyroclastic Flow Pyroclastic Surge Tephra Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
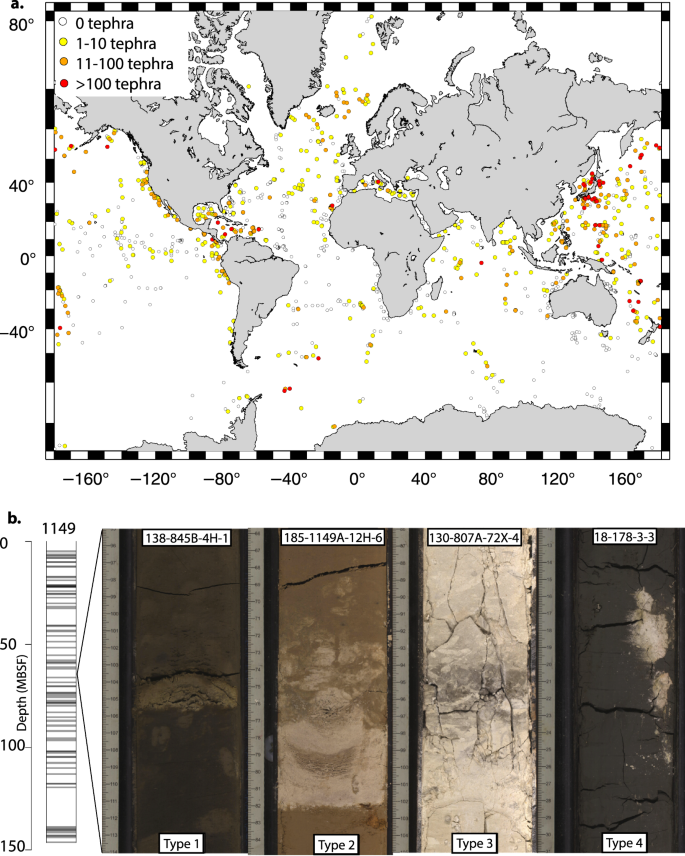
Volcore A Global Database Of Visible Tephra Layers Sampled By Ocean Drilling Scientific Data

Light Microscope Images Illustrating Tephra Shards Found In Europe A Download Scientific Diagram

Comparison Of Eruption Sizes Using Volume Of Magma Erupted U S Geological Survey
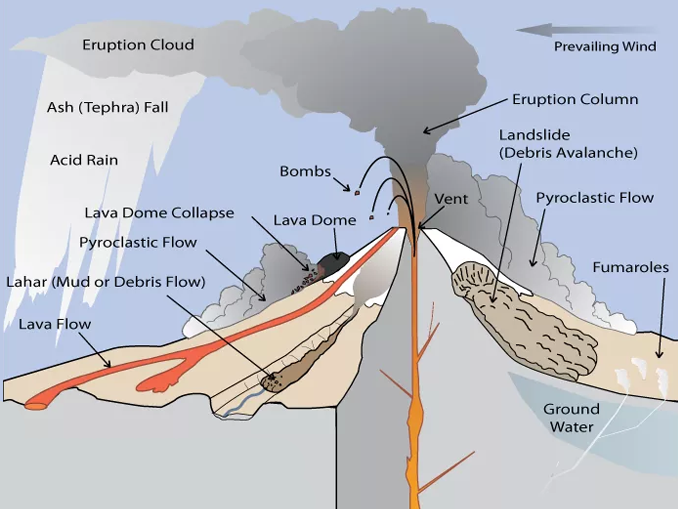
13 Parts Of A Volcano The Anatomy Of Volcanoes Earth How

Introduction Professional Paper 1563 Pre 1980 Tephra Fall Deposits Mount St Helens Washington
Types Of Volcanic Rocks Lava And Deposits Lucky Sci
Tephra Fall At Tungurahua Volcano Ecuador 1999 2014 An Example Of Tephra Accumulation From A Long Lasting Eruptive Cycle
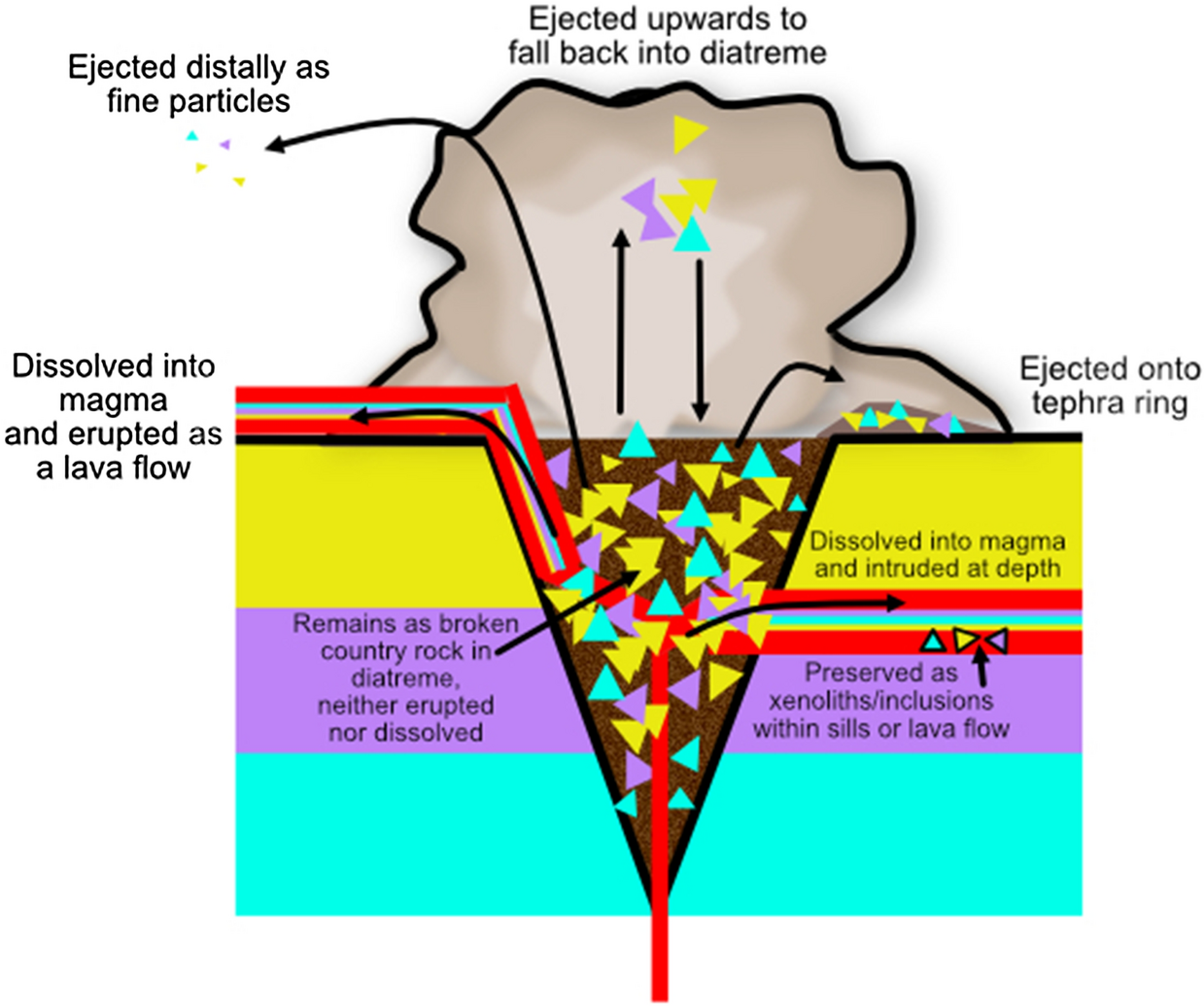
A Compilation And Characterisation Of Lithics In Kimberlite And Common Maar Diatremes And Tephra Ring Deposits Scientific Reports

Comments
Post a Comment